US Unemployment - Cost of Inflation Targeting
By Raulin Cadet | Published Dec. 25, 2023 | Updated Dec. 25, 2023 | Topics: Inflation, USA, Unemployment, Monetary policy, Federal Reserve Bank
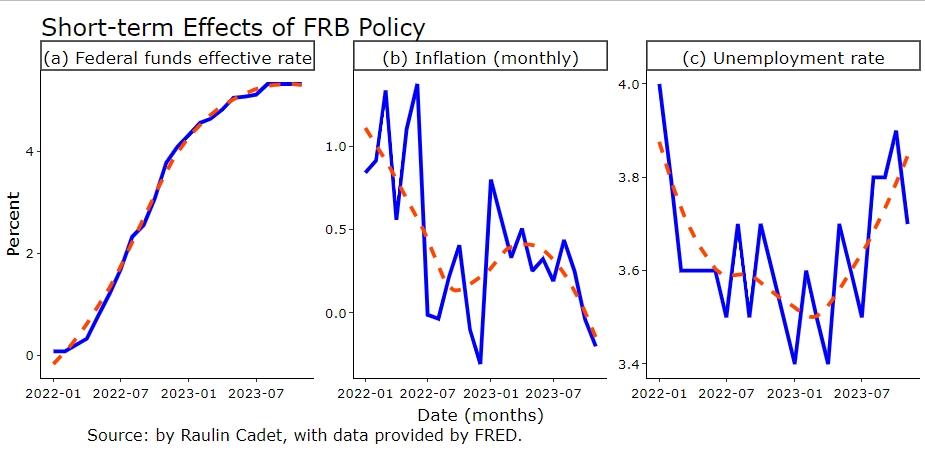
Following multiple increases in the funds rate by the Federal Reserve Bank (FRB), the trend of the unemployment rate ceases to decline and instead tends to rise. Does the Federal Reserve Bank policy achieve its goal? In fact, its goal was to bring inflation down to the 2% target level.
Definition: An inflation target is a precise annual inflation goal that a central bank aims to achieve. Considering this, the monetary policy of the central bank aims to enable the FRB of the United States to achieve its target of 2%.
One of the central bank's problems is that, in tackling inflation, it often leads in rising unemployment. This dilemma is explained by the economic framework known as the Phillips curve, which states that the unemployment rate tends to rise while the inflation rate is decreasing. With the goal to lower the inflation rate, the central bank has to be careful to cease raising interest rates when appropriate.
Why does the central bank raise interest rates in order to combat inflation? The interest paid on the loan increases as the interest rate rises. In such a scenario, loans typically decline. Global demand for products and services tends to decline in parallel with a decline in loans. When demand falls, prices tend to fall as well. For this reason, a rise in interest rates by the central bank usually results in a drop in inflation. But when demand declines, companies usually reduce production to match the decline. Additionally, companies tend to reduce production when interest rates rise because investments become more expensive. As a result, the same policies that are employed to reduce inflation also tend to raise unemployment.
The graphic of the current blog post shows the increasing trend (in orange color) of the effective funds rate of the Federal Reserve Bank, from January 2222 to November 2023. The graph shows that, as expected, the annual inflation rate has been falling while the funds rate has been rising. Despite the slow responsiveness of the unemployment rate, there is a minor tendency for the unemployment rate to rise.
The Federal Reserve's interest rate will remain high, between 5.25% and 5.5%, as approved by the board of governors in December 2023. As a result, one can expect the unemployment rate to increase.