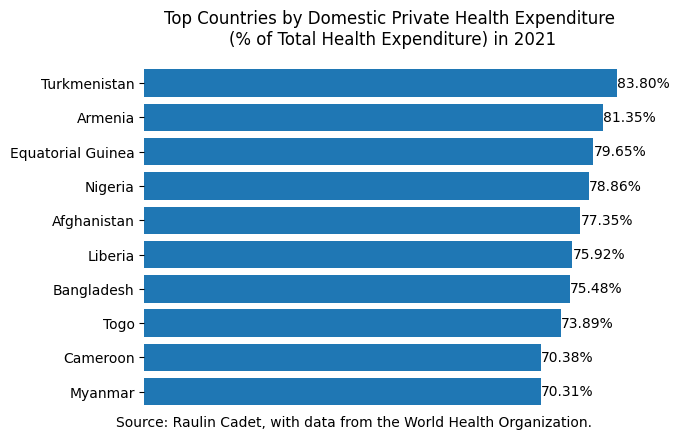
Top 10 Countries: Private Health Spending
By Raulin Cadet | Published Aug. 27, 2024 | Updated Aug. 27, 2024 | Topics: Health, Health cost, Human capital
The greatest wealth is health.
— Virgil
Humans are fundamental to the economy, serving both as consumers and as an essential element in the production of goods and services. Considered as a form of capital, the need for the proper training and good health of individuals is crucial for economic growth. However, the healthcare market often faces significant challenges, including high costs and limited accessibility.
To mitigate the adverse impact of health costs on the population, governments usually contribute to financing health services. However, domestic private expenditures remain high in some countries, particularly those with low income levels. This post presents the top 10 countries with the highest percentage of domestic private expenditures.
Definition: As defined by the World Health Organization, Domestic private health expenditure (PVT-D) as percentage of current health expenditure (CHE) is the percentage of health expenses from private domestic sources. This indicator shows how much local households, businesses, and charities contribute to healthcare. This includes both insurance payments and direct out-of-pocket costs.
The graphic in this post illustrates the high percentage of domestic private health expenditure in certain countries. The top two countries, Turkmenistan and Armenia, have percentages exceeding 80%. All ten countries shown have percentages above 70%. This indicates low government funding in these countries, which suggests inadequate access to healthcare services and potentially poor quality. High domestic private expenditures often mean that low-income households face significant barriers to obtaining care, and when they do, the quality may suffer due to systemic inefficiencies resulting from low government funding.
Addressing these high private health expenditures is essential for enhancing healthcare accessibility and quality, particularly in lower-income countries.